Lesson 25: Acoustic Immittance
Ipsilateral MEMR
Stapedius contraction measured in the same ear that received the acoustic stimulus.
Acoustic Delay
A condition identified during acoustic reflex threshold testing when a prolonged contraction cannot be sustained.
Tympanometric Width
Refers to the spread or broadness of the peak of the tympanogram.
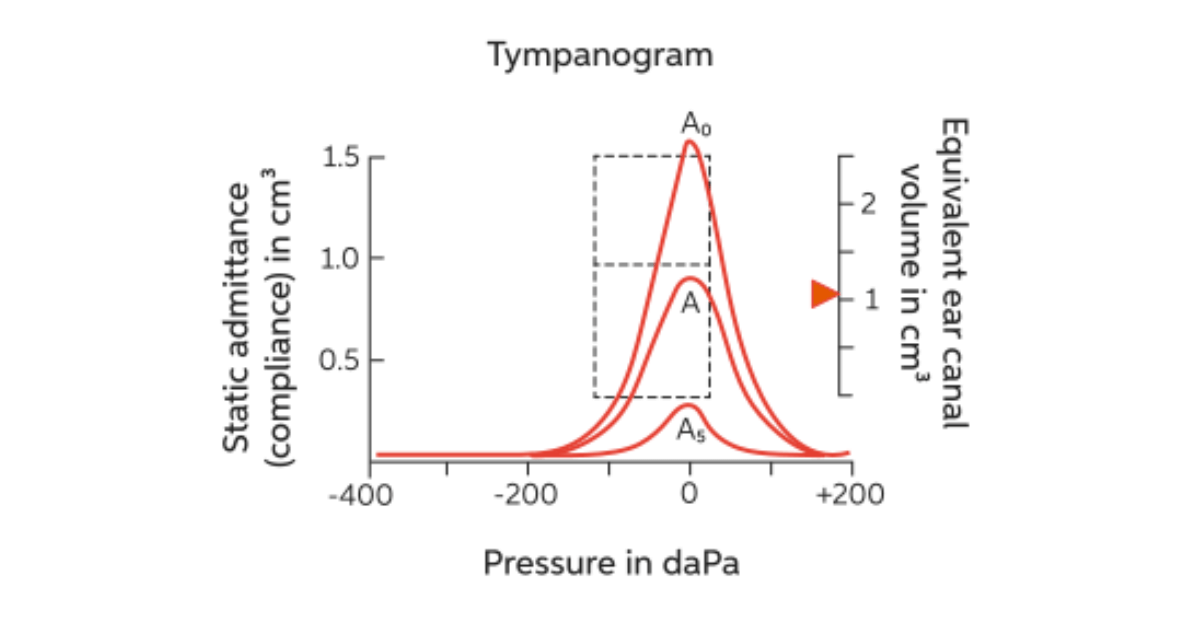
Tympanogram
A visual representation of the measurements taken during tympanometry such as compliance, PMC, TPP, ECV, and tympanometric width.
Middle ear muscle reflex (MEMR)
Also called the acoustic reflex and the stapedial reflex; represents the involuntary contraction of the stapedius muscle in response to intense sound.
cm3 (centimeters cubed)
The abbreviation for the physical units of impedance/stiffness used in tympanometry.
Acoustic admittance
The ease with which energy flows through the middle ear system.
Immittance meter/ Tympanometer
Equipment which enables the hearing aid specialist to perform specific tests involving middle ear function. Can be desktop or handheld.
Immittance Audiometry/ Tympanometry
One component of immittance; the measurement of middle ear function in terms of compliance/stiffness as a function of external ear canal pressure.
Probe Assembly and Probe Tip
The multi-purpose immittance assembly inserted into the ear canal; it uses a disposable or multi-use tip that provides an airtight seal when inserted properly.
Type A tympanogram
Normal middle ear compliance, peak pressure, and tympanometric width.
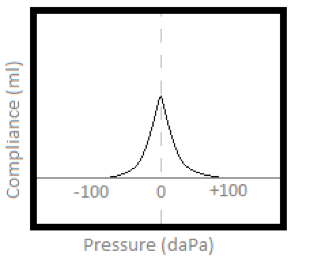
Mobility
The ease with which acoustic energy flows through the middle ear system to the cochlea, also called compliance or admittance.
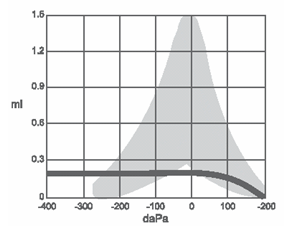
Type B tympanogram
Low compliance, no point of maximum compliance, normal ear canal volume.
Acoustic Impedence
The resistance to energy flow through the middle ear system.
mm H2O
The abbreviation for a physical unit of pressure called millimeters of water; used in tympanometry (see daPa which is used interchangably with mm H2O).
External ear canal volume (ECV)
Representation of the physical volume of the ear canal from the tip of the immittance probe to the tympanic membrane or beyond.
Contralateral MEMR
Stapedius contraction measured in the ear that is not receiving the acoustic stimulus.
daPa (decaPascals)
The abbreviation for a physical unit of pressure called the decaPascal; 1 daPa equals 10 Pascals; used in tympanometry (see mm H2O which is used interchangably with daPa).
mmho (millimho)
Unit of measurement for compliance on the vertical axis of the tympanogram. mmho are thousandths of an mho.
Point of maximum compliance (PMC)
The highest point of compliance in the tympanogram.
Type As tympanogram
Abnormally low compliance, normal peak pressure, and normal tympanometric width.
MEMR Decay
The measurement of the stapedius muscle’s ability to maintain a contraction to a sustained pure tone.
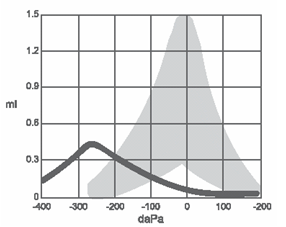
Type C tympanogram
Normal compliance, markedly negative tympanometric peak pressure, and normal tympanometric width.
Type Ad tympanogram
Abnormally high compliance, normal peak pressure, and normal tympanometric width.
MEMR Threshold
The lowest intensity of a pure tone that causes the stapedius muscle to contract.
Compliance
The ease with which acoustic energy flows through the middle ear system to the cochlea, also called mobility or admittance. Low compliance is high stiffness and high compliance is low stiffness.
Acoustic reflex threshold
Another imminence procedure besides tympanometry. Measures the threshold for the acoustic activation of the acoustic reflex.
Manometer
A component in the imittance meter that measures external ear canal pressure during tympanometry.
Tympanometric peak pressure (TPP)
The pressure associated with the point of maximum compliance.